Operating and safety instructions for bonded and reinforced abrasives (cutting and grinding discs)
Cutting and grinding discs
Abrasive discs can generate dangerous situations and/or create accidents if not use correctly. Read carefully the following information and the labels’ indications; operators instructed to use abrasive product; operators must comply with the laws and decrees of their country and the safety/operating instructions of the machines on which abrasive wheels are mounted. Do not allow untrained/incompetent operators to use abrasive wheels. Abrasive wheels are relatively fragile: handle and use with care. The use of damaged wheels, incorrectly used and the incorrectly installation can cause accidents, damages and serious injuries to persons. Cutting, grinding and polishing applications can free hazardous contaminants in the air. Use appropriate powder/fume suction systems and wear protection devices for respiratory tract.
Expiry:
Lifetime of resin-bonded abrasive wheels is 3 years from production date if reinforced (BF on label) or 2 years if without reinforcement (B on the label). The expiry date can be shown on the boxes, on the central metal hub or through cuts on the label perimeter. Never use expired wheels. ELITE abrasives are manufactured according the following norms: EN12413 (Europe), ANSI B7.1 (USA), AS 1788.1 (Australia), MPA or OSA.
Checking, transport, handling and storage:
Verify packaging damages; refuse damaged packagings; handle with care and avoid shocks; store at temperatures between 5°C and 45°C and relative humidity between 45% and 65%; do not expose wheels to frost and high humidity conditions, water or chemical products such as solvents. Always use oldest wheels, but make sure they are not expired. To help make the right choice, see cutting range here, or grinding range here.


Wheel inspection:
Before mounting the disc, make sure it is not cracked or damaged. Do not use wheels if damaged (like DIAG.3 - fig.7) or expired. Carry out a sound check by striking one side of the disc with a non metallic object (screwdriver handle). If the sound is damp and not clear, reject the wheel.Do not use wheels that were exposed to too high/too low temperatures/humidity or that have been artificially or accidentally wet.
Machine inspection:
Check flanges, backing pads, support pivots and adapters. Make sure the grinder is suitable for the type of work to be made and that the wheel is adequate for the grinder. Always use with suitable safety guard (fig.6). Always direct the open part of the safety guard to a direction opposite to the operator. Keep machines in an efficient state.
Eyes, face and body protection:
- Always use eye and face protection such as mask, screen and glasses (fig.2), hat or head protection, protective clothing, and safety shoes.
- The noise generated by coated abrasive products can exceed 80 dB, meaning prolonged exposure can cause permanent damage to hearing. Use ear protection such as earplugs and anti-noise screen (fig.3).
- The vibrations generated by coated abrasive products can cause damage to the human body so make sure you adopt work turnovers and resting breaks.
- Carry out a specific evaluation of the noise and vibration risk and adopt suitable protection and precautions.
- Wear protective gloves that fully cover wrists (fig.4).


- Carry out an evaluation of the physical and chemical risks associated with the use of abrasive products and adopt suitable precautions and protective measures.
- Protect the respiratory tract by wearing a mask with specific filters or air respirator systems.
- Use protective measures of the working environment such as ventilation, filtration and powder/fume suction systems (fig.5).
- Nearby personnel must be protected with all the above precautions/measures.
Assembly instructions:
- Follow the assembly instructions supplied with the machine and the use restrictions shown on the wheel label (fig.1).
- Make sure the maximum turning speed (RPM) of the machine is always, in any operating condition, lower than or equal to the speed shown on the wheel label.
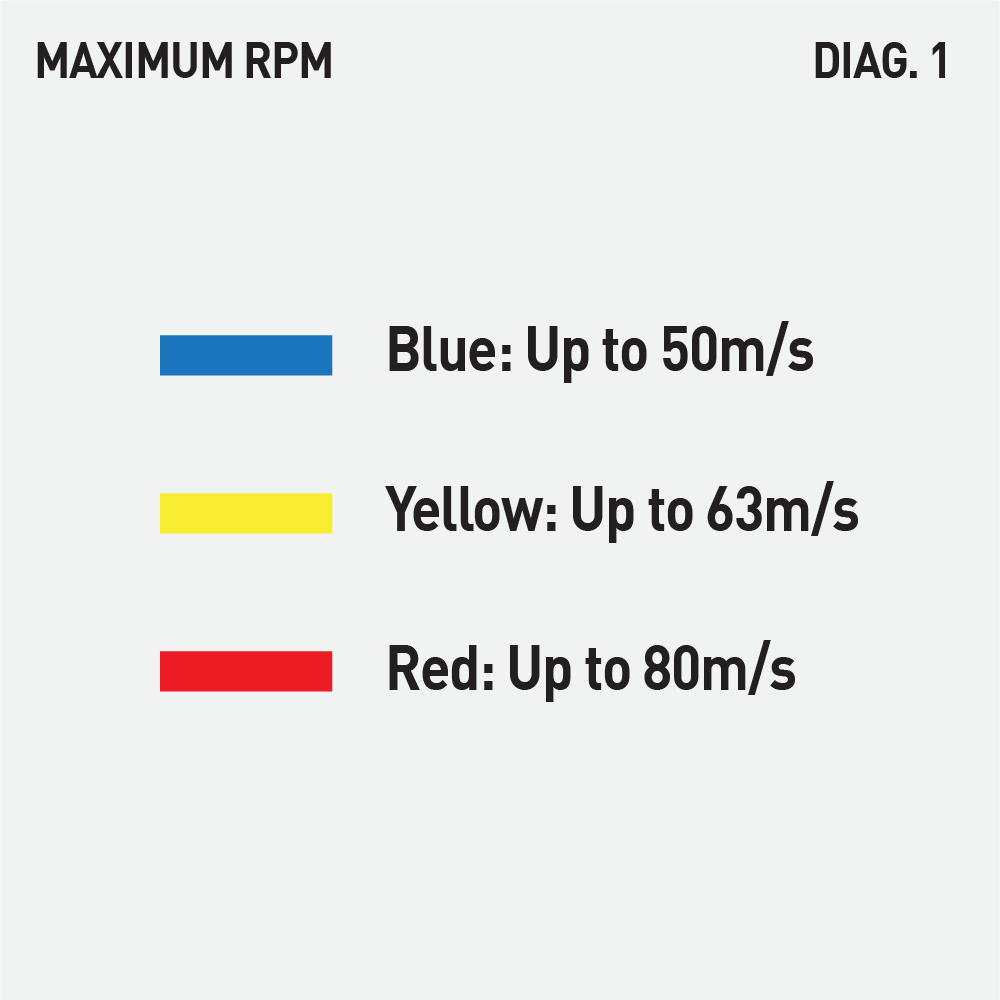
- A transversal coloured stripe on the wheel label indicates also its operating peripheral speed according to: DIAG.1
- Check that dimensions and shape of the wheel correspond to those allowed for the machine.
- Check that the wheel is wholly contained within the safety guard of the grinder.
- Do not modify the clamping flanges. Before mounting or dismounting an abrasive wheel, disconnect the power supply (electric energy, compressed air, etc.).

- Do not force wheels during assembly.
- Avoid clamping with too high tightening torque. Once the wheel is installed, make sure that it rotates freely by turning it by hand.
- Check the presence, correct installation and securing of the safety guard.
- Connect the power supply, start the machine and make it turn for at least 30 sec.
During this test, do not keep the open area of the safety guard oriented towards the operator and other personnel. In case anomalies, vibrations, irregular rotation should occur, let the grinder stop naturally, disconnect power supply, remove the wheel and check its assembly. If the problem persists, reject the wheel and inform the supplier of the problem. Some types of wheels can be supplied with mounting blotters that have to be mounted between the flanges and each side of the disc to compensate slight irregularities of surfaces between flanges and wheels.
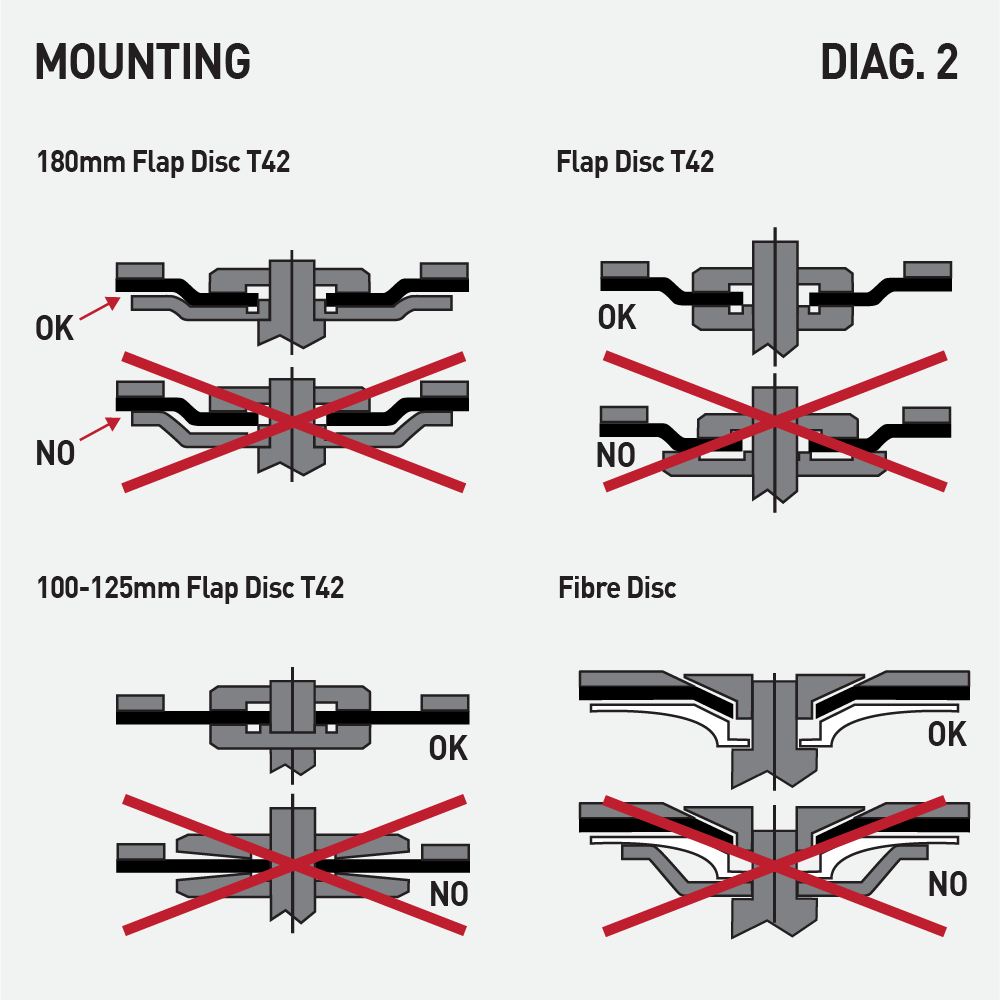
Clamping flanges:
Make sure the flanges are flat, clean and smooth. Always use suitable flanges ( DIAG.2 ). Flanges must have the same diameter and the same shape (recesses) towards both faces of the wheel; make exception the raised hub flanges (mod. 1 of DIAG.2).
Flanges diameter: for cutting and grinding wheels is normally equal to 1/3 of the wheel diameter. Make exception: reinforced depressed center grinding wheels (Type 27), reinforced conical (Type 28), semi-flexible reinforced (Type 29), reinforced depressed centre cutting wheels (Type 42) and flat (Type 41) up to diameter 230mm, that must have the following flanges diameters:
- 19mm (wheel diam. ≤100mm and bore ≤10mm )
- 32mm (wheel diam. ≤100mm and bore between 10 and 16mm)
- 41mm (wheel diam. between 100 and 230mm, bore 22.23mm).

Indications shown on wheel label:
- Specifications characterizing the wheel: wheel dimension;
- Type of abrasive (A, Z, C); granulometry of the abrasive (16,...,100 grit).
- Hardness: scale of toughness shown with letters from A (very soft) to Z (very hard).
- Resin binder shown by “B’’ and reinforcement structure shown by “F’’ on label.
- Maximum allowed turning speed (RPM) and maximum allowed peripheral speed (m/s): the most common peripheral speeds are 50-63-80-100m/s.
Reference norms: EN12413, ANSI B7.1, etc.
Indications on the workable materials: steel, aluminum, cast iron, stainless steel, stone, marble, etc.
Pictograms ( DIAG.3 ): from (fig.1) to (fig.7) explained above; (fig.8) do not use for side grinding; (fig.9) do not use on portable machines (wheels made only for stationary machines); (fig.10) not suitable for wet grinding/cutting; (fig.11) only suitable for wet grinding/cutting.
Shape types ( DIAG.4 ): (Type 1) straight grinding wheel; (Type 27) depressed centre grinding wheel; (Type 28) conical grinding wheel; (Type 29) depressed centre semiflexible grinding wheel; (Type 41) flat cutting wheel; (Type 42) depressed centre cutting wheel.

 Need assistance?
Need assistance?




